PHP 7 is a dynamic scripting langauge for delivering applications. You can get 2x faster performance and 50% better memory consumption than PHP 5.6, allowing you to serve more concurrent users without adding any hardware. However, PHP 7 not included with Debian 8.x stable version. In this tutorial, you will learn about installing PHP 7 on Debian 8.6 server. Please note that Debian 9.0 “Stretch” will include PHP 7 by default.
Related: How to install PHP 7 on Ubuntu Linux 14.04 LTS
Steps to install PHP 7 on Debian 8.6
- First, remove old PHP 5.6
- Configure dotdeb is an extra repository for PHP 7
- Install PHP 7
- Reconfigure web server
- Restart web server
To list your Debian version, enter:
$ lsb_release -a
No LSB modules are available.
Distributor ID: Debian
Description: Debian GNU/Linux 8.6 (jessie)
Release: 8.6
Codename: jessie
Use the following syntax to save existing config files:
$ sudo tar zcvf /root/etc.backup.tar.gz /etc/
Step #1: Delete old php 5.6 (if installed)
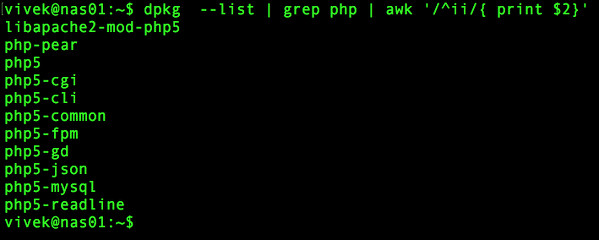
First, list all installed old php 5.x packages, enter:
$ dpkg --list | grep php | awk '/^ii/{ print $2}'
Sample outputs:
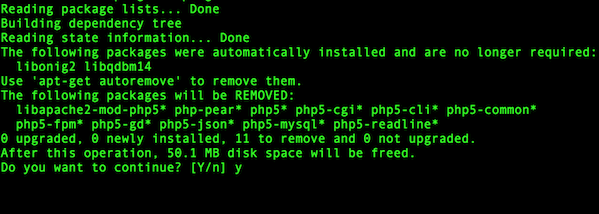
To delete old php 5.6 packages, enter:
$ x="$(dpkg --list | grep php | awk '/^ii/{ print $2}')"
$ sudo apt-get --purge remove $xSample outputs:
Step #2: Configure dotdeb
Dotdeb is an extra repository providing up-to-date packages (such as PHP 7 and more) for your Debian servers. It supports both Debian 8.x “Jessie” and Debian 7.x “Wheezy”.
Configuration for Debian 8.x “Jessie”
Append the following two lines to /etc/apt/sources.list as root user::
$ sudo -s
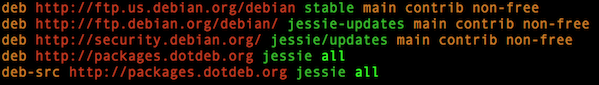
# echo 'deb http://packages.dotdeb.org jessie all' >> /etc/apt/sources.list
# echo 'deb-src http://packages.dotdeb.org jessie all' >> /etc/apt/sources.list
Save and close the file. Here is my updated file:
$ cat /etc/apt/sources.list
Sample outputs:
Configuration for Debian 7.x “Wheezy”
Append the following two lines to /etc/apt/sources.list as root user:
$ sudo -s
# echo 'deb http://packages.dotdeb.org wheezy all' >> /etc/apt/sources.list
# echo 'deb-src http://packages.dotdeb.org wheezy all' >> /etc/apt/sources.list
Save and close the file.
Step #3: Fetch and install the GnuPG key
Type the following commands
$ cd /tmp
$ wget https://www.dotdeb.org/dotdeb.gpg
$ sudo apt-key add dotdeb.gpg
$ rm dotdeb.gpg
Refresh apt database to include new packages:
$ sudo apt-get update
Sample outputs:
Get:1 http://security.debian.org jessie/updates InRelease [63.1 kB]
Ign http://ftp.us.debian.org stable InRelease
Get:2 http://packages.dotdeb.org jessie InRelease [9,840 B]
Hit http://ftp.debian.org jessie-updates InRelease
Hit http://ftp.us.debian.org stable Release.gpg
Get:3 http://packages.dotdeb.org jessie/all Sources [30.0 kB]
Get:4 http://ftp.debian.org jessie-updates/main amd64 Packages/DiffIndex [5,932 B]
Hit http://ftp.us.debian.org stable Release
Get:5 http://security.debian.org jessie/updates/main amd64 Packages [313 kB]
Hit http://ftp.debian.org jessie-updates/contrib amd64 Packages
Hit http://ftp.us.debian.org stable/main amd64 Packages
Get:6 http://packages.dotdeb.org jessie/all amd64 Packages [111 kB]
Get:7 http://ftp.debian.org jessie-updates/non-free amd64 Packages/DiffIndex [736 B]
Hit http://ftp.us.debian.org stable/contrib amd64 Packages
Get:8 http://security.debian.org jessie/updates/contrib amd64 Packages [2,506 B]
Hit http://ftp.debian.org jessie-updates/contrib Translation-en
Hit http://ftp.us.debian.org stable/non-free amd64 Packages
Get:9 http://ftp.debian.org jessie-updates/main Translation-en/DiffIndex [2,704 B]
Get:10 http://security.debian.org jessie/updates/non-free amd64 Packages [14 B]
Get:11 http://security.debian.org jessie/updates/contrib Translation-en [1,211 B]
Hit http://ftp.us.debian.org stable/contrib Translation-en
Get:12 http://ftp.debian.org jessie-updates/non-free Translation-en/DiffIndex [736 B]
Get:13 http://security.debian.org jessie/updates/main Translation-en [168 kB]
Hit http://ftp.us.debian.org stable/main Translation-en
Get:14 http://security.debian.org jessie/updates/non-free Translation-en [14 B]
Hit http://ftp.us.debian.org stable/non-free Translation-en
Ign http://packages.dotdeb.org jessie/all Translation-en_IN
Ign http://packages.dotdeb.org jessie/all Translation-en
Fetched 708 kB in 10s (69.8 kB/s)
Reading package lists... Done
|
Step #4: Install PHP 7
You created a shell variable called $x in step #1. To install equivalent of php5 packages, enter:
$ y="$(sed 's/php5/php7.0/g' <<<$x)"
$ echo Old PHP5 packages name: $x
Old PHP5 packages name: libapache2-mod-php5 php-pear php5 php5-cgi php5-cli php5-common php5-fpm php5-gd php5-json php5-mysql php5-readline
$ echo New PHP7 packages name: $y
New PHP7 packages name: libapache2-mod-php7.0 php-pear php7.0 php7.0-cgi php7.0-cli php7.0-common php7.0-fpm php7.0-gd php7.0-json php7.0-mysql php7.0-readline
$ sudo apt-get install $y
Sample outputs:
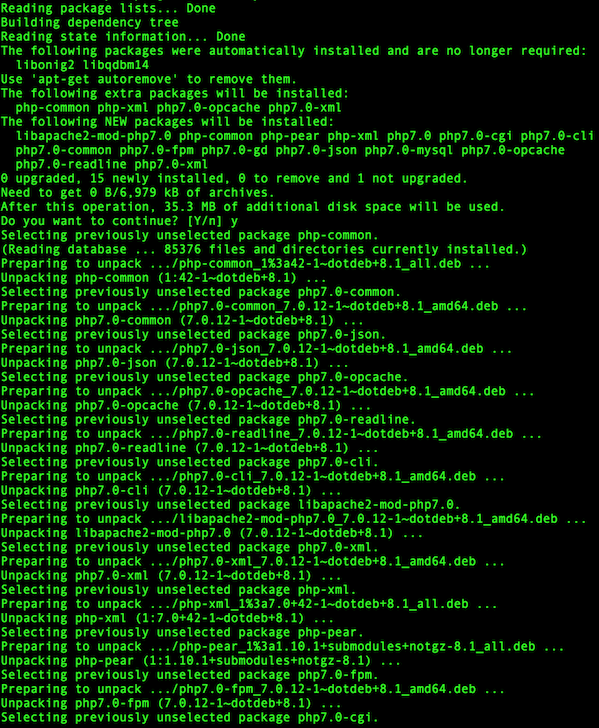
Fig.04: Installing PHP7 on my Debain 8.6 server
How do I search PHP7 packages?
$ apt-cache search php7.0-\*
$ apt-cache search php7.0-\* | grep -i mysql
Sample outputs from 1st command:
libapache2-mod-php7.0 - server-side, HTML-embedded scripting language (Apache 2 module)
libphp7.0-embed - HTML-embedded scripting language (Embedded SAPI library)
php-all-dev - package depending on all supported PHP development packages
php7.0 - server-side, HTML-embedded scripting language (metapackage)
php7.0-apcu - APC User Cache for PHP
php7.0-apcu-bc - APCu Backwards Compatibility Module
php7.0-bcmath - Bcmath module for PHP
php7.0-bz2 - bzip2 module for PHP
php7.0-cgi - server-side, HTML-embedded scripting language (CGI binary)
php7.0-cli - command-line interpreter for the PHP scripting language
php7.0-common - documentation, examples and common module for PHP
php7.0-curl - CURL module for PHP
php7.0-dba - DBA module for PHP
php7.0-dbg - Debug symbols for PHP7.0
php7.0-dev - Files for PHP7.0 module development
php7.0-enchant - Enchant module for PHP
php7.0-fpm - server-side, HTML-embedded scripting language (FPM-CGI binary)
php7.0-gd - GD module for PHP
php7.0-geoip - GeoIP module for PHP
php7.0-gmp - GMP module for PHP
php7.0-igbinary - igbinary serializer for PHP
php7.0-imagick - Provides a wrapper to the ImageMagick library
php7.0-imap - IMAP module for PHP
php7.0-interbase - Interbase module for PHP
php7.0-intl - Internationalisation module for PHP
php7.0-json - JSON module for PHP
php7.0-ldap - LDAP module for PHP
php7.0-mbstring - MBSTRING module for PHP
php7.0-mcrypt - libmcrypt module for PHP
php7.0-memcached - memcached extension module for PHP, uses libmemcached
php7.0-mongodb - MongoDB driver for PHP
php7.0-msgpack - MessagePack serializer for PHP
php7.0-mysql - MySQL module for PHP
php7.0-odbc - ODBC module for PHP
php7.0-opcache - Zend OpCache module for PHP
php7.0-pgsql - PostgreSQL module for PHP
php7.0-phpdbg - server-side, HTML-embedded scripting language (PHPDBG binary)
php7.0-pspell - pspell module for PHP
php7.0-readline - readline module for PHP
php7.0-recode - recode module for PHP
php7.0-redis - PHP extension for interfacing with Redis
php7.0-snmp - SNMP module for PHP
php7.0-soap - SOAP module for PHP
php7.0-sqlite3 - SQLite3 module for PHP
php7.0-ssh2 - Bindings for the libssh2 library
php7.0-sybase - Sybase module for PHP
php7.0-tidy - tidy module for PHP
php7.0-xdebug - Xdebug Module for PHP
php7.0-xml - DOM, SimpleXML, WDDX, XML, and XSL module for PHP
php7.0-xmlrpc - XMLRPC-EPI module for PHP
php7.0-xsl - XSL module for PHP (dummy)
php7.0-zip - Zip module for PHP
|
How do I install PHP7 packages individually?
Alternatively, you can just install needed PHP7 packages. In this example, install php7, php-fpm, php7-mysql and php7-gd:
$ sudo apt-get install php7.0 php7.0-fpm php7.0-gd php7.0-mysql
Step #5: Reconfigure web server and php 7
Your php7 config files are located in /etc/php/7.0/ directory as follows:
- /etc/php/7.0/apache2/ – PHP 7 with Apache 2
- /etc/php/7.0/fpm/ – PHP 7 fpm for Nginx/Lighttpd/Apache2 and other server.
- /etc/php/7.0/mods-available/ – All php ini config file for PHP modules such as gd/mysql/memecached and others.
You need to edit files and configure a web-server as per your setup.
Examples: Configure Lighttpd web-server to use PHP 7
Edit the /etc/lighttpd/conf-enabled/15-fastcgi-php.conf file, enter:
$ sudo vi /etc/lighttpd/conf-enabled/15-fastcgi-php.conf
Append/edit as follows (note updated /run/php/php7.0-fpm.sock path):
fastcgi.server += ( ".php" =>
((
"bin-path" => "/usr/bin/php-cgi",
"socket" => "/run/php/php7.0-fpm.sock",
"max-procs" => 1,
"bin-environment" => (
"PHP_FCGI_CHILDREN" => "4",
"PHP_FCGI_MAX_REQUESTS" => "10000"
),
"bin-copy-environment" => (
"PATH", "SHELL", "USER"
),
"broken-scriptfilename" => "enable"
))
)
|
Save and close the file. Restart web-server as per step #6.
Examples: Configure Nginx web-server to use PHP 7
Edit the /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/default file, enter:
$ sudo vi /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/default
First add the following at the top of file:
# Upstream to abstract backend connection(s) for PHP 7.
upstream myphpsevenbackend {
server unix:/run/php/php7.0-fpm.sock;
}
|
Next, locate the server block and update/edit/append as follows:
# Pass all .php files onto a php-fpm/php-fcgi server. #
index index.php;
location ~ [^/]\.php(/|$) {
fastcgi_split_path_info ^(.+?\.php)(/.*)$;
if (!-f $document_root$fastcgi_script_name) {
return 404;
}
# This is a robust solution for path info security issue and works with "cgi.fix_pathinfo = 1" in php.ini (default) #
include /etc/nginx/fastcgi_params;
fastcgi_index index.php;
fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME $document_root$fastcgi_script_name;
fastcgi_pass myphpsevenbackend;
}
|
Save and close the file. Restart web-server as per step #6.
Examples: Configure Apache 2 web-server to use PHP 7
To enable PHP 7.0 FPM in Apache2, enter:
$ sudo a2enmod proxy_fcgi setenvif
Considering dependency proxy for proxy_fcgi:
Enabling module proxy.
Enabling module proxy_fcgi.
Module setenvif already enabled
To activate the new configuration, you need to run:
service apache2 restart
$ sudo a2enconf php7.0-fpm
Enabling conf php7.0-fpm.
To activate the new configuration, you need to run:
service apache2 reload
Restart web-server as per step #6.
Step #6: Restart web server
If you are using lighttpd web-server, enter:
$ sudo systemctl restart lighttpd.service
If you are using Nginx web-server, enter:
$ sudo systemctl restart nginx.service
If you are using Apache 2 web-server, enter:
$ sudo systemctl reload apache2.service
Test your setup
Create a file called test.php in your DocumentRoot (e.g. /var/www/html/test.php):
<?php
/* test.php */
phpinfo();
?>
|
Save and close the file. Fire a web-browser and type url:
http://your-domain/test.php
OR
http://server.ip.address.here/test.php
Sample outputs:
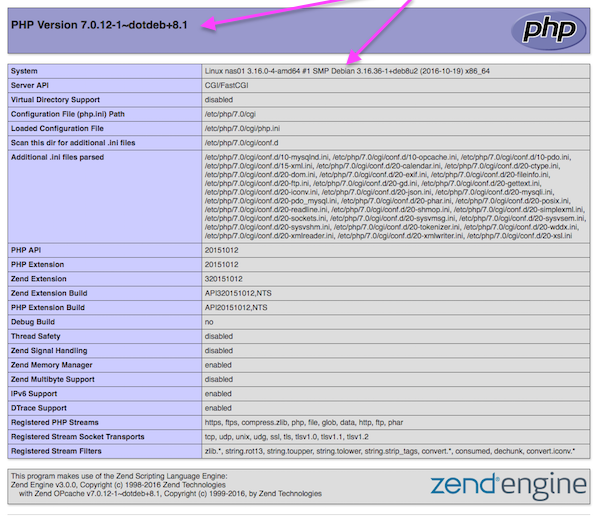
Fig.05: phpinfo() in action displaying info about PHP 7
How do I stop/start/restart php7.0-fpm?
The syntax is as follows
$ sudo systemctl stop php7.0-fpm.service
$ sudo systemctl start php7.0-fpm.service
$ sudo systemctl restart php7.0-fpm.service
$ sudo systemctl reload php7.0-fpm.service
A note about php7.0-fpm configuration file
- /etc/php/7.0/fpm/php.ini – PHP 7 configuration file.
- /etc/php/7.0/fpm/php-fpm.conf – PHP 7 FPM Configuration file.
- /etc/php/7.0/fpm/pool.d/www.conf – Default pool for PHP 7 FPM. Here you can define user/group, FastCGI request path, process manager and children values, php error file, memory limit and much more.
Whenever you made changes to any one of the above file(s), reload/restart php7.0-fpm.service using the following syntax:
$ sudo systemctl reload php7.0-fpm.service
So there you have it, a PHP 7 enabled and configured on Debian Linux 7.x or 8.x server successfully.